Zyan Disassembler Engine (Zydis)
Fast and lightweight x86/x86-64 disassembler library.
Features
- Supports all x86 and x86-64 (AMD64) instructions.
- Supports pretty much all ISA extensions (list incomplete):
- FPU (x87), MMX
- SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, SSE4A, AESNI
- AVX, AVX2, AVX512BW, AVX512CD, AVX512DQ, AVX512ER, AVX512F, AVX512PF, AVX512VL
- ADX, BMI1, BMI2, FMA, FMA4
- Optimized for high performance
- No dynamic memory allocation ("malloc")
- Very small file-size overhead compared to other common disassembler libraries
- Complete doxygen documentation
- No dependencies on platform specific APIs
- Should compile on any platform with a complete libc and CMake
- Tested on Windows, macOS and Linux
Roadmap
- Language bindings [v2.0 final]
- Tests [v2.0 final]
- Graphical editor for the instruction-database [v2.0 final]
- Implement CMake feature gates. Currently, everything is always included. [v2.0 final]
- Encoding support [v2.1]
Quick Example
The following example program uses Zydis to disassemble a given memory buffer and prints the output to the console.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Zydis/Zydis.h>
int main()
{
uint8_t data[] =
{
0x51, 0x8D, 0x45, 0xFF, 0x50, 0xFF, 0x75, 0x0C, 0xFF, 0x75,
0x08, 0xFF, 0x15, 0xA0, 0xA5, 0x48, 0x76, 0x85, 0xC0, 0x0F,
0x88, 0xFC, 0xDA, 0x02, 0x00
};
// Initialize decoder context.
ZydisDecoder decoder;
&decoder,
// Initialize formatter. Only required when you actually plan to
// do instruction formatting ("disassembling"), like we do here.
ZydisFormatter formatter;
ZydisFormatterInit(&formatter, ZYDIS_FORMATTER_STYLE_INTEL);
// Loop over the instructions in our buffer.
uint64_t instructionPointer = 0x007FFFFFFF400000;
uint8_t* readPointer = data;
size_t length = sizeof(data);
ZydisDecodedInstruction instruction;
&decoder, readPointer, length, instructionPointer, &instruction)))
{
// Print current instruction pointer.
printf("%016" PRIX64 " ", instructionPointer);
// Format & print the binary instruction
// structure to human readable format.
char buffer[256];
&formatter, &instruction, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
puts(buffer);
readPointer += instruction.length;
length -= instruction.length;
instructionPointer += instruction.length;
}
}
ZYDIS_EXPORT ZydisStatus ZydisDecoderDecodeBuffer(const ZydisDecoder *decoder, const void *buffer, size_t bufferLen, uint64_t instructionPointer, ZydisDecodedInstruction *instruction)
Decodes the instruction in the given input buffer.
ZYDIS_EXPORT ZydisStatus ZydisDecoderInit(ZydisDecoder *decoder, ZydisMachineMode machineMode, ZydisAddressWidth addressWidth)
Initializes the given ZydisDecoder instance.
ZYDIS_EXPORT ZydisStatus ZydisFormatterInit(ZydisFormatter *formatter, ZydisFormatterStyle style)
Initializes the given ZydisFormatter instance.
@ ZYDIS_FORMATTER_STYLE_INTEL
Generates intel-style disassembly.
Definition: Formatter.h:60
ZYDIS_EXPORT ZydisStatus ZydisFormatterFormatInstruction(const ZydisFormatter *formatter, ZydisDecodedInstruction *instruction, char *buffer, size_t bufferLen)
Formats the given instruction and writes it into the output buffer.
#define ZYDIS_SUCCESS(status)
Checks if a zydis operation was successfull.
Definition: Status.h:157
Master include file, including everything else.
uint8_t length
The length of the decoded instruction.
Definition: DecoderTypes.h:752
Sample Output
The above example program generates the following output:
007FFFFFFF400000 push rcx
007FFFFFFF400001 lea eax, [rbp-0x01]
007FFFFFFF400004 push rax
007FFFFFFF400005 push qword ptr [rbp+0x0C]
007FFFFFFF400008 push qword ptr [rbp+0x08]
007FFFFFFF40000B call [0x008000007588A5B1]
007FFFFFFF400011 test eax, eax
007FFFFFFF400013 js 0x007FFFFFFF42DB15
Compilation
Zydis builds cleanly on most platforms without any external dependencies. You can use CMake to generate project files for your favorite C99 compiler.
# Linux and OS X
git clone 'https://github.com/zyantific/zydis.git'
cd zydis
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
ZydisInfo tool
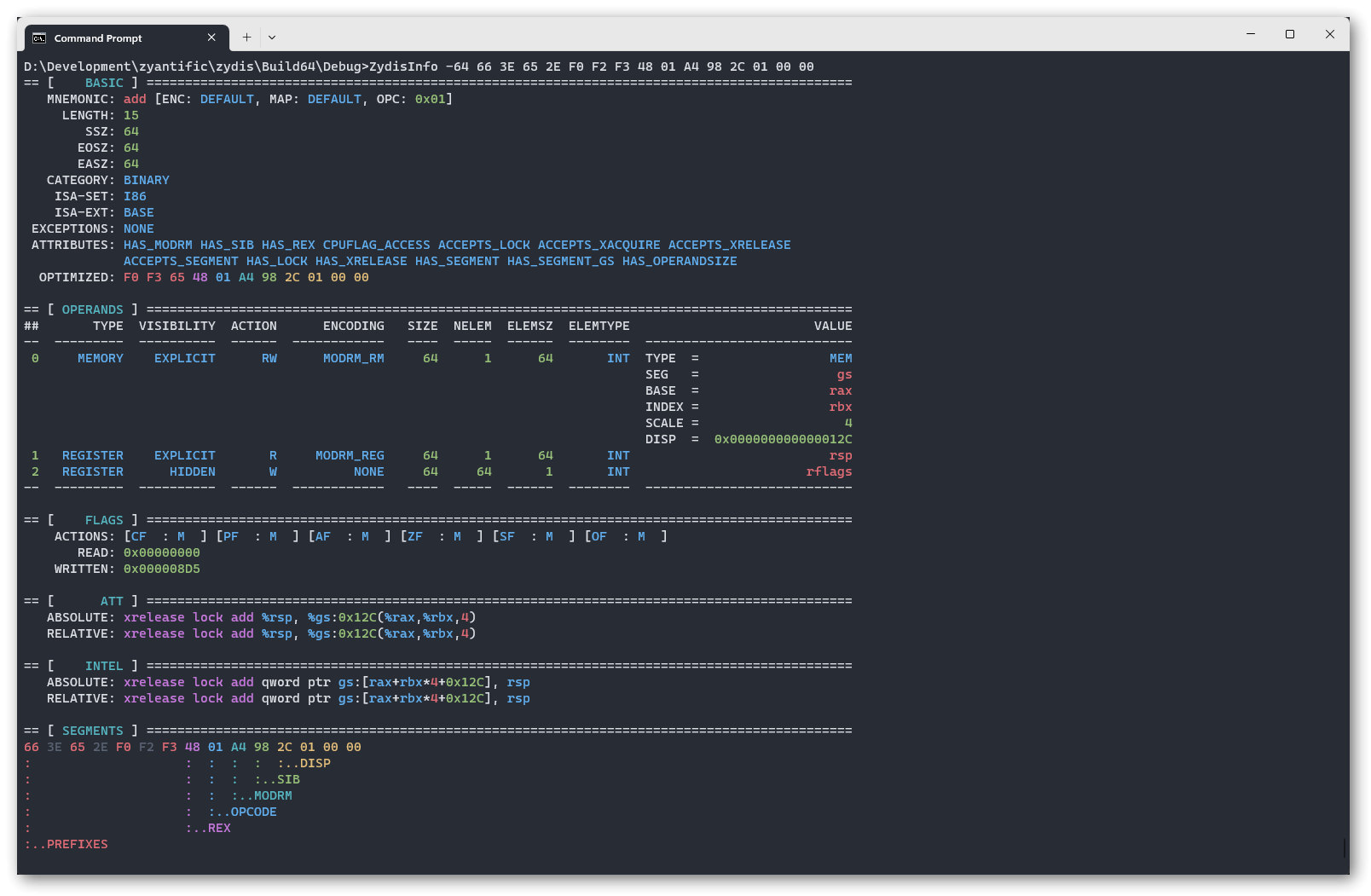
Credits
- Intel (for open-sourcing XED, allowing for automatic comparision of our tables against theirs, improving both)
- LLVM (for providing pretty solid instruction data as well)
- Christian Ludloff (http://sandpile.org, insanely helpful)
- Our contributors on GitHub
License
Zydis is licensed under the MIT license.
